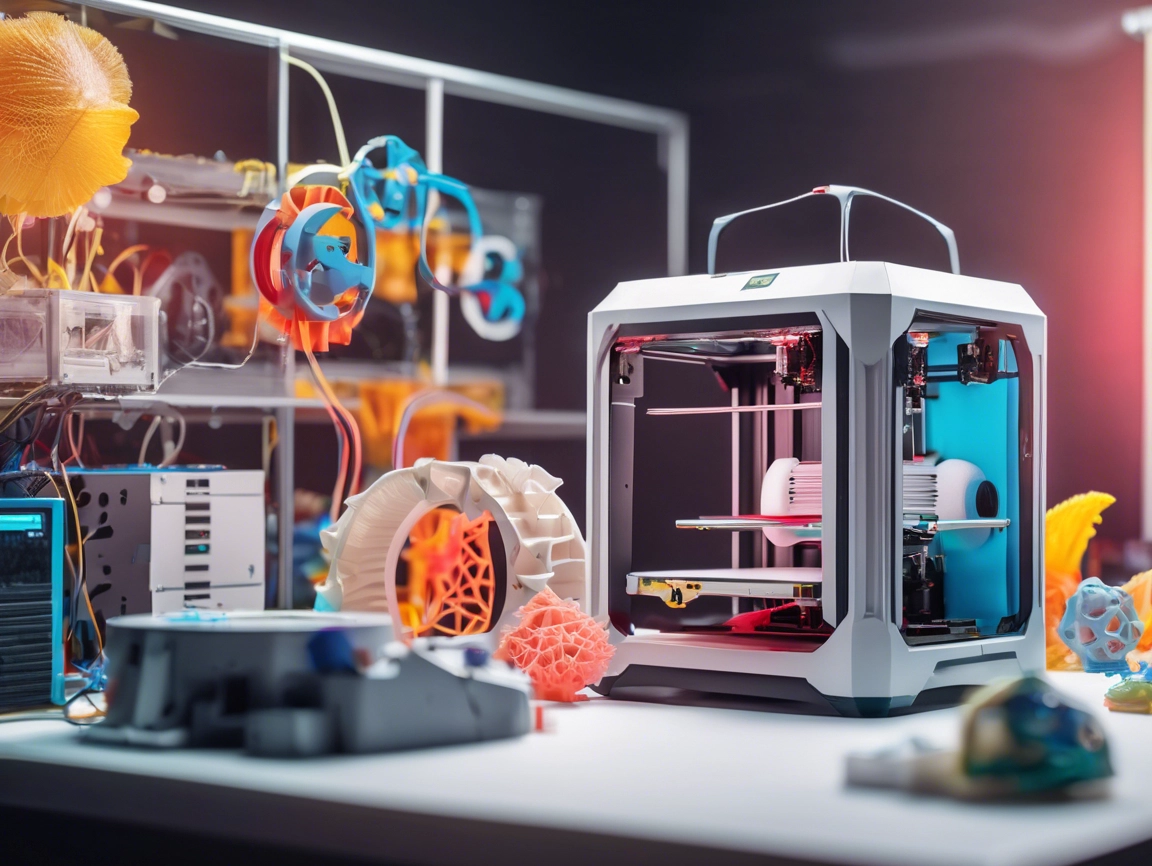
As technology continues to evolve and innovate, one of the most exciting areas of development is in the realm of 3D printing. With the ability to create complex shapes and structures with unprecedented precision, it’s no wonder that 3D printers are becoming increasingly popular among hobbyists, professionals, and entrepreneurs alike.
Understanding the Basics
Before we dive into the world of 3D printing technologies, let’s start by understanding what 3D printing is. In simple terms, 3D printing is a process where a digital design is translated into a physical object layer by layer. The most common types of 3D printing technologies are Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
FDM: The Most Affordable Option
One of the most popular and affordable options is FDM, also known as fused filament fabrication. This type of printer uses a hot extruder to deposit melted plastic layer by layer, building up complex shapes and structures. FDM is one of the most accessible forms of 3D printing, making it a great option for beginners.
The Pros and Cons of FDM
While FDM is an excellent choice for beginners, there are some limitations to consider:
- Limited detail: FDM prints can be rough and lack the level of detail found in other technologies.
- Layer lines: The layering process can result in visible lines on the final product.
- Material limitations: FDM typically uses plastic filaments, which may not be suitable for certain applications.
SLA: The Ultimate in Detail
For those seeking incredible detail and accuracy, SLA is the way to go. This technology uses a laser to solidify liquid resin layer by layer, creating smooth, featureless surfaces with high accuracy. SLA printers are ideal for producing models that require intricate details or small features.
The Pros and Cons of SLA
While SLA offers incredible detail, there are some trade-offs to consider:
- High cost: SLA printers are generally more expensive than FDM options.
- Limited build volume: SLA printers typically have a smaller build volume than FDM options.
- Resin limitations: SLA uses liquid resin, which can be prone to warping or cracking.
SLS: The Strongest and Most Durable
For those seeking durability and strength, SLS is the way to go. This technology uses a laser to fuse together tiny particles of powdered material, building up complex shapes and structures. SLS printers are ideal for producing parts that require high strength and stiffness.
The Pros and Cons of SLS
While SLS offers incredible durability, there are some trade-offs to consider:
- High cost: SLS printers are generally more expensive than FDM options.
- Limited build volume: SLS printers typically have a smaller build volume than FDM options.
- Material limitations: SLS requires powdered material, which can be limited in terms of color and texture.
Conclusion
In conclusion, each of these 3D printing technologies has its own unique strengths and weaknesses. Whether you’re looking for affordability, detail, or durability, there’s a 3D printer out there that’s right for you. By understanding the pros and cons of each technology, you can make an informed decision about which option is best for your needs.
Call to Action
Ready to start your 3D printing journey? Which technology do you think will be the best fit for your needs? Let us know in the comments below!